Embark on an in-depth exploration of oral and topical medication administration posttest, a crucial aspect of healthcare practice. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of proper medication administration, providing healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills to ensure patient safety and optimal outcomes.
The following sections will provide a thorough overview of oral and topical medication administration, encompassing the different types of medications, step-by-step administration procedures, common challenges and errors, medication safety principles, patient education strategies, and the importance of accurate documentation. By the end of this posttest, healthcare professionals will gain a deep understanding of these essential concepts, enabling them to deliver safe and effective medication administration to their patients.
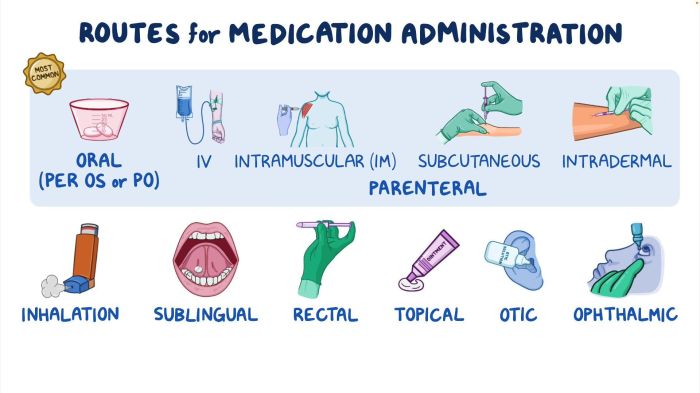
Oral Medication Administration

Proper oral medication administration is crucial for ensuring optimal patient outcomes. It involves the correct administration of oral medications, including tablets, capsules, liquids, and suspensions.
To administer oral medications effectively, follow these steps:
- Verify the patient’s identity and the medication order.
- Explain the purpose of the medication to the patient.
- Position the patient comfortably and ensure their ability to swallow.
- Administer the medication with water or as directed by the order.
- Observe the patient for any immediate adverse reactions.
Common Challenges and Errors, Oral and topical medication administration posttest
- Medication errors due to misidentification or incorrect dosage.
- Patient refusal or inability to swallow.
- Failure to provide adequate patient education.
Topical Medication Administration

Topical medications are applied directly to the skin, mucous membranes, or hair. They are used to treat a variety of conditions, including infections, inflammation, and skin disorders.
Different types of topical medications include:
- Creams
- Lotions
- Ointments
- Powders
- Gels
- Solutions
To administer topical medications, follow these steps:
- Verify the patient’s identity and the medication order.
- Clean and dry the affected area.
- Apply the medication as directed by the order.
- Cover the area with a bandage or dressing if necessary.
- Monitor the patient for any adverse reactions.
Common Challenges and Errors, Oral and topical medication administration posttest
- Skin irritation or allergic reactions.
- Incorrect application or dosage.
- Failure to protect the treated area from contamination.
Medication Safety
Medication safety is paramount in healthcare to prevent medication errors and adverse events. It involves the implementation of systems and processes to ensure the safe and effective use of medications.
Principles of medication safety include:
- Accurate prescribing and dispensing.
- Proper administration and monitoring.
- Effective patient education.
- Regular medication reviews.
- Reporting and analysis of adverse events.
Tips for ensuring medication safety:
- Use standardized medication orders.
- Implement barcode scanning systems.
- Provide comprehensive patient education.
- Encourage patient involvement in medication management.
Patient Education: Oral And Topical Medication Administration Posttest

Patient education is essential for empowering patients to manage their medications effectively and safely. It involves providing clear and concise information about medications, including their purpose, dosage, side effects, and precautions.
Tips for educating patients about medication administration:
- Use simple and understandable language.
- Provide written instructions and materials.
- Answer patient questions thoroughly.
- Encourage patients to ask questions and report any concerns.
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in patient education by:
- Providing accurate and up-to-date information.
- Encouraging open communication.
- Empowering patients to make informed decisions about their medication use.
Documentation
Proper documentation of medication administration is essential for legal and ethical reasons. It provides a record of the medications given to the patient, the time of administration, and the person who administered them.
Guidelines for documenting medication administration:
- Document the patient’s name, date, and time of administration.
- Record the name, dosage, and route of administration of the medication.
- Note any patient responses or adverse reactions.
- Sign and date the documentation.
Legal and ethical implications of proper documentation:
- Protects healthcare professionals from legal liability.
- Provides evidence of medication administration for reimbursement purposes.
- Ensures continuity of care by providing a clear record of the patient’s medication history.
FAQ Overview
What is the most important aspect of medication administration?
Ensuring patient safety by administering medications accurately and appropriately.
What are the key principles of medication safety?
The “five rights” of medication administration: right patient, right medication, right dose, right route, and right time.
Why is patient education essential in medication administration?
It empowers patients to actively participate in their own care, understand their medications, and adhere to their treatment plans.