Embark on a captivating journey with “Drag the Labels to Identify the Constituent Parts of Blood.” This interactive exploration unravels the intricate components that make up this vital fluid, providing a profound understanding of its significance in maintaining our health.
Delve into the realm of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma, discovering their unique structures, functions, and roles in sustaining life.
Introduction
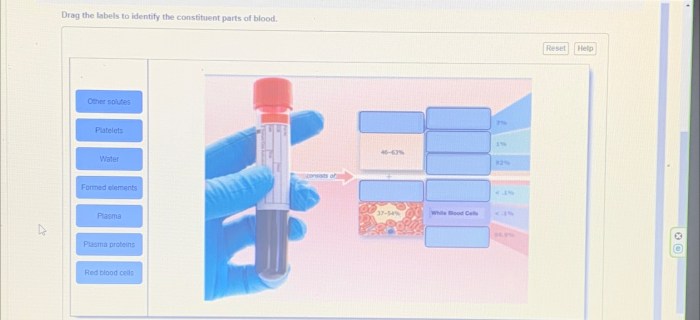
Blood is a complex fluid that circulates throughout the body, performing vital functions for survival. It is composed of various components, each with distinct roles and characteristics. Understanding the constituent parts of blood is crucial for comprehending its functions and maintaining overall health.
Red Blood Cells
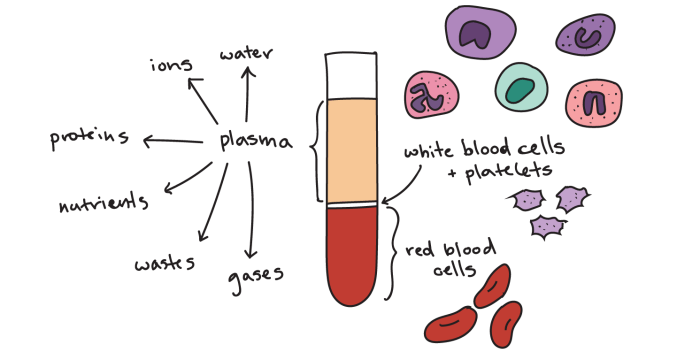
Red blood cells are the most abundant blood component, responsible for oxygen transport throughout the body. They contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen molecules and facilitates their delivery to tissues. Red blood cells have a biconcave shape, which increases their surface area for efficient oxygen exchange.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells are part of the immune system and play a critical role in defending the body against infections and foreign invaders. There are several types of white blood cells, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type has specific functions in recognizing and eliminating pathogens or harmful substances.
Platelets
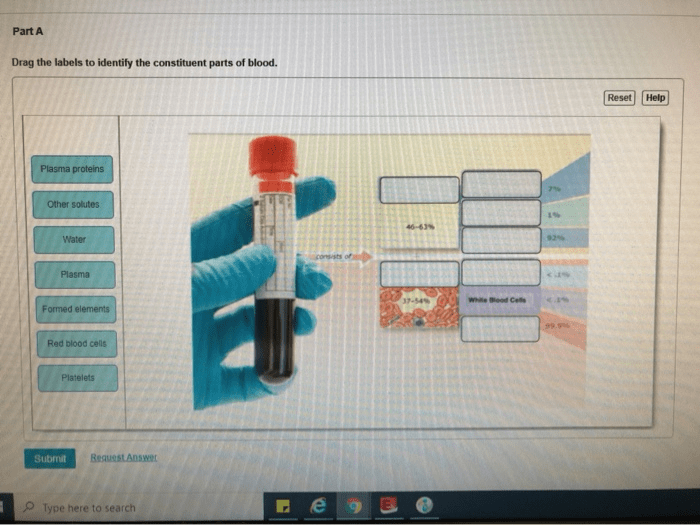
Platelets are small, disk-shaped blood cells that are essential for blood clotting. When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets aggregate and form a clot to prevent excessive bleeding. They contain proteins and enzymes that initiate and stabilize the clotting process.
Plasma: Drag The Labels To Identify The Constituent Parts Of Blood
Plasma is the liquid component of blood that makes up approximately 55% of its volume. It contains water, electrolytes, proteins, hormones, and other substances. Plasma maintains blood volume, regulates fluid balance, and transports nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
Blood Typing
Blood is classified into different types based on the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. The two main blood group systems are the ABO system and the Rh system. Blood typing is essential for blood transfusions to ensure compatibility between donors and recipients.
Blood Disorders
Various blood disorders can affect the production, function, or composition of blood components. Common blood disorders include anemia, leukemia, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease. These disorders can cause a range of symptoms, from fatigue and weakness to life-threatening complications. Treatment options vary depending on the specific disorder.
FAQ Summary
What is the primary function of red blood cells?
Transporting oxygen throughout the body.
How do white blood cells contribute to our health?
They defend against infections and foreign invaders.
What is the role of platelets in blood clotting?
They aggregate to form a clot, preventing excessive bleeding.