Which of the following statements is true of cytokinesis? This fundamental question delves into the intricate world of cell division, a process essential for growth, development, and the very existence of life. As we embark on this exploration, we will unravel the secrets of cytokinesis, deciphering its mechanisms, significance, and implications.
Cytokinesis, the final stage of cell division, orchestrates the physical separation of the duplicated genetic material into two distinct daughter cells. This intricate process ensures the faithful transmission of genetic information and the maintenance of cellular integrity. Throughout this discourse, we will delve into the diverse mechanisms employed by animal and plant cells to achieve cytokinesis, exploring the captivating roles of contractile rings, cell plates, and microtubules.
Cytokinesis in Animal Cells
Cytokinesis is the process of dividing the cytoplasm of a cell into two daughter cells. In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs through a process called cleavage furrowing, which is driven by a contractile ring composed of actin and myosin filaments.The contractile ring forms at the equator of the cell and constricts, pinching off the plasma membrane and dividing the cell into two.
The different stages involved in cytokinesis in animal cells are:
- Prophase:The chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase:The chromosomes align at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase:The chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in.
- Cytokinesis:The contractile ring forms and constricts, dividing the cell into two.
Comparison of Cytokinesis in Animal and Plant Cells
| Feature | Animal Cells | Plant Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Contractile ring | Yes | No |
| Cell plate | No | Yes |
| Microtubules | Guide the formation of the contractile ring | Form the phragmoplast, which guides the formation of the cell plate |
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells
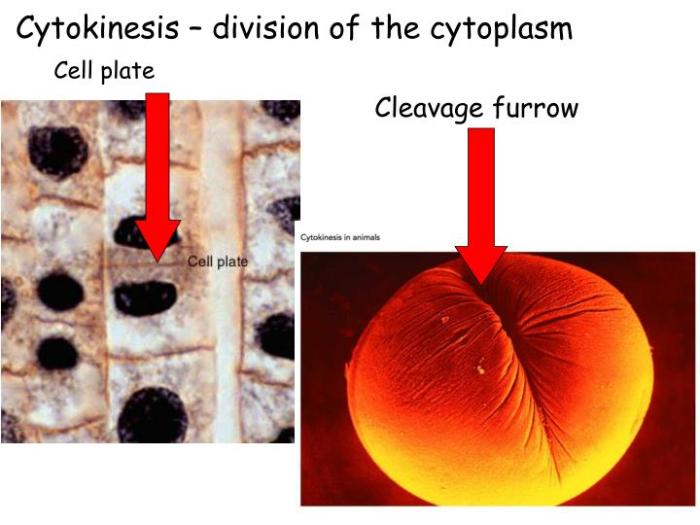
In plant cells, cytokinesis occurs through a process called cell plate formation. The cell plate is a new cell wall that forms between the two daughter cells.The cell plate is formed from vesicles that are transported to the equator of the cell by microtubules.
The vesicles fuse together to form a continuous cell wall.The different stages involved in cytokinesis in plant cells are:
- Prophase:The chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase:The chromosomes align at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase:The chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes.
- Cytokinesis:The cell plate forms between the two daughter cells.
Role of Microtubules in Plant Cell Cytokinesis
Microtubules play a crucial role in plant cell cytokinesis. They form the phragmoplast, which is a spindle-shaped structure that guides the formation of the cell plate. The phragmoplast is composed of two sets of microtubules that overlap at the equator of the cell.
The microtubules in the phragmoplast are oriented perpendicular to the cell plate and help to transport the vesicles that form the cell plate to the equator of the cell.
Regulation of Cytokinesis
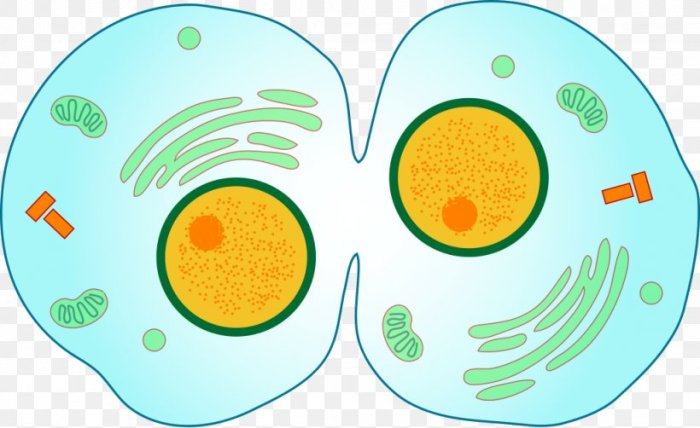
Cytokinesis is regulated by a number of factors, including:
- The cell cycle:Cytokinesis is triggered by the cell cycle checkpoint at the end of anaphase.
- The mitotic spindle:The mitotic spindle helps to position the chromosomes and the contractile ring.
- The cell cortex:The cell cortex is a network of actin filaments that helps to constrict the cell during cytokinesis.
- Proteins:A number of proteins are involved in regulating cytokinesis, including:
- RhoA:A small GTPase that activates the contractile ring.
- Myosin II:A motor protein that drives the constriction of the contractile ring.
- Anillin:A scaffolding protein that helps to organize the contractile ring.
Checkpoints in Cytokinesis, Which of the following statements is true of cytokinesis
There are two checkpoints in cytokinesis:
- The spindle assembly checkpoint:This checkpoint ensures that all of the chromosomes are properly attached to the mitotic spindle before anaphase begins.
- The cytokinesis checkpoint:This checkpoint ensures that the contractile ring is properly formed and positioned before cytokinesis begins.
Errors in Cytokinesis
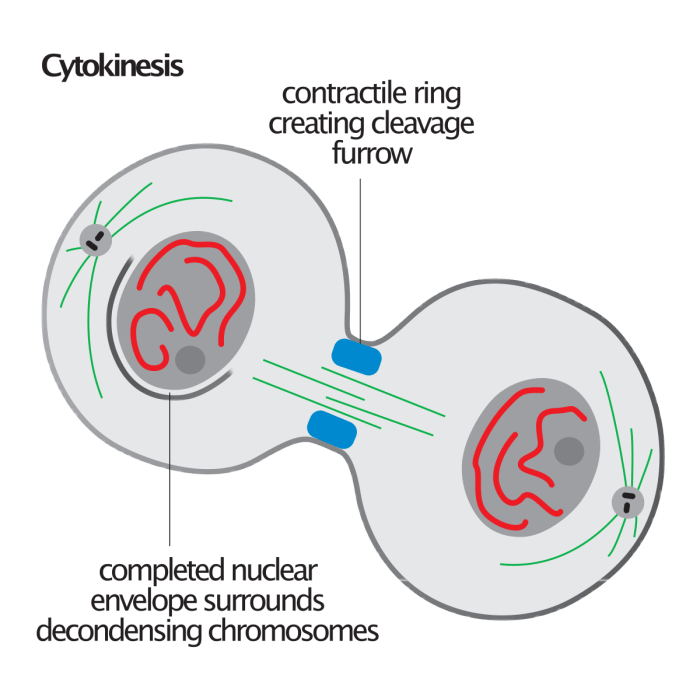
Errors in cytokinesis can lead to a number of problems, including:
- Multinucleated cells:These cells have more than one nucleus.
- Micronuclei:These are small, extra nuclei that are often found in cancer cells.
- Aneuploidy:This is a condition in which a cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes.
Errors in cytokinesis can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Mutations in genes that regulate cytokinesis
- Exposure to toxins
- Mechanical stress
Errors in cytokinesis can contribute to the development of cancer. For example, aneuploidy is a common feature of cancer cells. Aneuploidy can lead to changes in gene expression, which can promote the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Question & Answer Hub: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Cytokinesis
What is the primary function of cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis is responsible for the physical separation of the duplicated genetic material into two distinct daughter cells, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information and the maintenance of cellular integrity.
How do animal and plant cells differ in their mechanisms of cytokinesis?
Animal cells employ a contractile ring composed of actin and myosin filaments to cleave the cell membrane, while plant cells form a cell plate, a new cell wall that grows inward from the center of the cell.
What are the potential consequences of errors in cytokinesis?
Errors in cytokinesis can lead to the formation of cells with abnormal chromosome numbers, which can contribute to genetic disorders, developmental abnormalities, and even cancer.