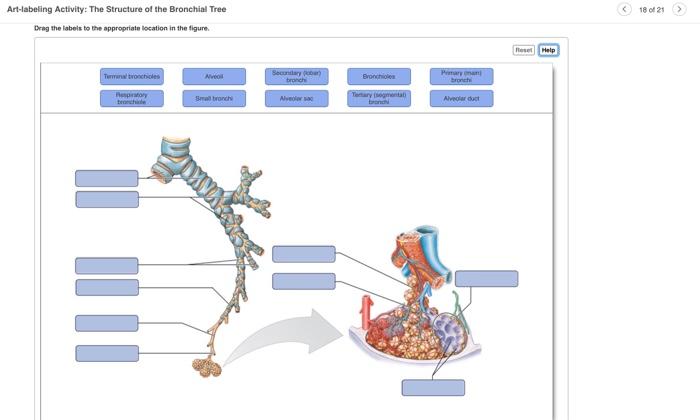
Art-labeling activity the structure of the bronchial tree – Embarking on an art-labeling activity that delves into the structure of the bronchial tree, this exploration unveils the intricate network of airways that facilitate respiration. From the trachea’s descent to the alveoli’s delicate exchange surfaces, this journey unveils the complexities of the respiratory system.
The bronchial tree’s hierarchical organization, branching patterns, and distinct sections are meticulously examined, providing a comprehensive understanding of its anatomy. Through engaging diagrams and tables, students actively engage in the labeling process, solidifying their knowledge of the bronchial tree’s major structures.
Anatomical Overview of the Bronchial Tree
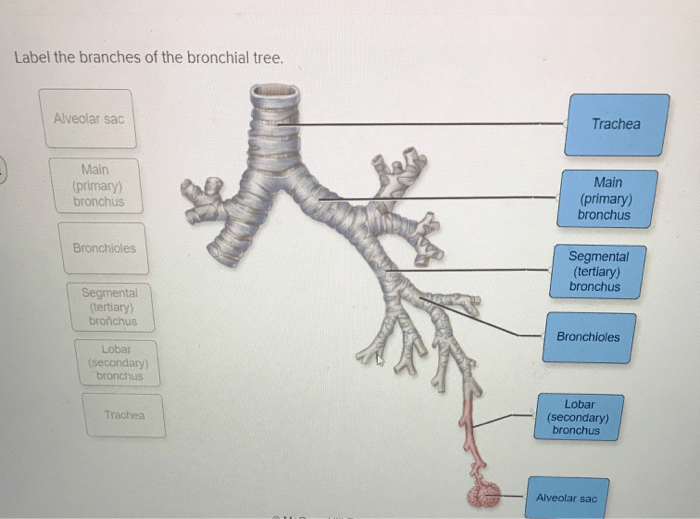
The bronchial tree is a complex system of branching airways that conducts air to and from the lungs. It begins with the trachea, which divides into the left and right primary bronchi. These primary bronchi enter the lungs and continue to divide into smaller and smaller branches, forming the bronchial tree.
Branching Pattern
The branching pattern of the bronchial tree is fractal, meaning it repeats itself at different scales. The trachea divides into two primary bronchi, each of which divides into three secondary bronchi. The secondary bronchi divide into tertiary bronchi, and so on.
This branching continues until the smallest airways, called bronchioles, are reached.
Sections of the Bronchial Tree
The bronchial tree can be divided into several sections based on the size and structure of the airways. The trachea and primary bronchi are considered the central airways. The secondary and tertiary bronchi are known as the lobar bronchi. The smaller airways, including the bronchioles and alveoli, are referred to as the peripheral airways.
- Trachea:The trachea is a large, cylindrical tube that extends from the larynx to the chest cavity. It is supported by cartilaginous rings that prevent it from collapsing.
- Primary bronchi:The primary bronchi are the two large branches of the trachea that enter the lungs. They are also supported by cartilaginous rings.
- Lobar bronchi:The lobar bronchi are the branches of the primary bronchi that supply air to the different lobes of the lungs. They are smaller in diameter than the primary bronchi and are supported by less cartilage.
- Bronchioles:The bronchioles are the smallest branches of the bronchial tree. They are not supported by cartilage and are lined with ciliated epithelium.
- Alveoli:The alveoli are the tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs. They are lined with capillaries, which allow oxygen to pass from the lungs into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to pass from the bloodstream into the lungs.
The bronchial tree is a complex and vital part of the respiratory system. It allows air to flow to and from the lungs, enabling us to breathe.
Labeling Activity
Diagram, Art-labeling activity the structure of the bronchial tree
The following diagram shows the major structures of the bronchial tree:

Instructions
- Label the following structures on the diagram:
- Trachea
- Primary bronchi
- Lobar bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Alveoli
- Submit your completed diagram to your instructor.
Clinical Significance
Understanding the structure of the bronchial tree is essential for diagnosing and treating respiratory conditions. For example, knowing the branching pattern of the airways can help doctors identify the location of a blockage or infection. Additionally, knowledge of the different sections of the bronchial tree can help doctors choose the appropriate treatment for a particular condition.
- Bronchoscopy:Bronchoscopy is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube is inserted into the bronchial tree to visualize the airways. This procedure can be used to diagnose and treat a variety of respiratory conditions, such as lung cancer, pneumonia, and asthma.
- Lung biopsy:A lung biopsy is a procedure in which a small sample of lung tissue is removed for examination under a microscope. This procedure can be used to diagnose a variety of respiratory conditions, such as lung cancer, sarcoidosis, and interstitial lung disease.
Comparison with Other Respiratory Structures
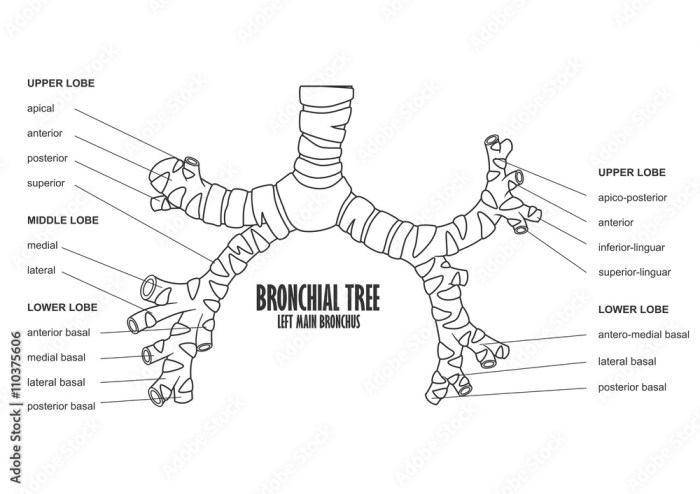
The bronchial tree is similar to other respiratory structures in that it is a system of branching airways that conducts air to and from the lungs. However, there are also some important differences between the bronchial tree and other respiratory structures.
- Nasal cavity:The nasal cavity is the first part of the respiratory tract. It is lined with mucus-producing cells that help to trap dust and other particles from entering the lungs. The nasal cavity also helps to warm and humidify the air that we breathe.
- Larynx:The larynx is the organ that produces sound. It is located at the top of the trachea and is made up of several cartilages, including the thyroid cartilage, the cricoid cartilage, and the arytenoid cartilages. The larynx also contains the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound.
The following table summarizes the similarities and differences between the bronchial tree, nasal cavity, and larynx:
| Structure | Function | Similarities | Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bronchial tree | Conducts air to and from the lungs |
|
|
| Nasal cavity | Filters, warms, and humidifies air |
|
|
| Larynx | Produces sound |
|
|
Artistic Representation: Art-labeling Activity The Structure Of The Bronchial Tree
The bronchial tree has been depicted in various forms of art, including paintings, sculptures, and photography. These artistic representations often highlight the intricate branching pattern of the airways and the vital role that the bronchial tree plays in the respiratory system.
- Painting:The painting “The Bronchial Tree” by Vincent van Gogh is a famous depiction of the bronchial tree. The painting shows the intricate branching pattern of the airways in great detail.
- Sculpture:The sculpture “The Bronchial Tree” by Henry Moore is a large-scale sculpture that depicts the bronchial tree in a simplified form.
The sculpture highlights the organic shape of the bronchial tree and its importance to the human body.
- Photography:The photograph “The Bronchial Tree” by Ernst Haeckel is a microscopic photograph of the bronchial tree. The photograph shows the intricate branching pattern of the airways in great detail.
These artistic representations of the bronchial tree help us to appreciate the beauty and complexity of the human body. They also remind us of the importance of the bronchial tree to our health and well-being.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of understanding the bronchial tree structure?
Understanding the bronchial tree structure is crucial for diagnosing and treating respiratory conditions, as it provides insights into the airflow patterns and potential obstructions within the airways.
How does the bronchial tree compare to other respiratory structures?
The bronchial tree exhibits unique branching patterns and hierarchical organization compared to other respiratory structures like the nasal cavity and larynx, reflecting its specialized role in gas exchange.
What are some artistic representations of the bronchial tree?
The bronchial tree has been depicted in various artistic forms, including paintings, sculptures, and photography, often highlighting its intricate beauty and physiological significance.