The Enlightenment icivics Answer Key unveils the captivating tale of the Enlightenment, an era that ignited the flames of intellectual revolution. This remarkable period witnessed the rise of brilliant minds who dared to challenge established norms and usher in an age of reason, liberty, and progress.
From the halls of academia to the corridors of power, the Enlightenment left an enduring mark on Western civilization. Its key figures, groundbreaking ideas, and far-reaching impact continue to resonate today, shaping our understanding of the world and our place within it.
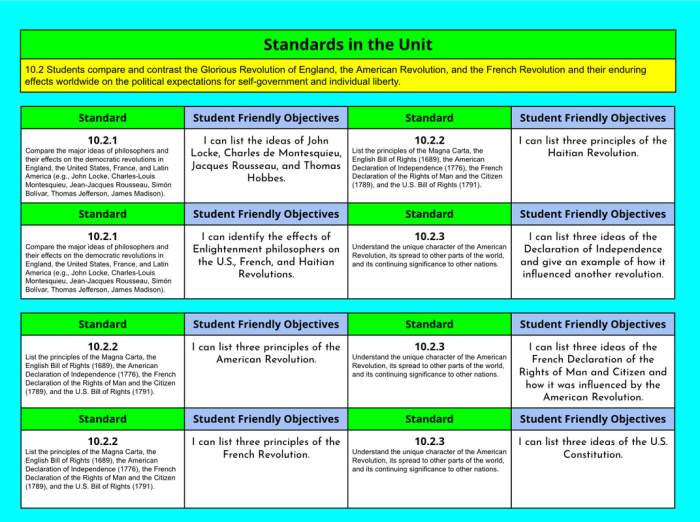
Definition and Context of the Enlightenment

The Enlightenment, also known as the Age of Reason, was an intellectual and philosophical movement that emerged in Europe during the 18th century. It was characterized by a belief in the power of human reason and the importance of scientific inquiry.
Enlightenment thinkers sought to challenge traditional beliefs and institutions, and to promote ideas of individual liberty, natural rights, and the separation of powers. Their ideas had a profound impact on the development of modern political and social thought.
Key Figures and Their Contributions
- John Locke: Developed the concept of natural rights and the social contract theory of government.
- Voltaire: Advocated for freedom of speech and religious tolerance.
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau: Emphasized the importance of individual freedom and the general will.
- Immanuel Kant: Developed the concept of categorical imperatives and the Enlightenment’s moral philosophy.
- Mary Wollstonecraft: Pioneered feminist thought and advocated for women’s rights.
Impact on Political and Social Thought, The enlightenment icivics answer key
The Enlightenment had a significant impact on political and social thought. It promoted the idea of natural rights, which are inherent and inalienable rights that belong to all individuals. This concept influenced the development of democratic governments and the protection of individual liberties.
Enlightenment thinkers also advocated for the separation of powers, which divides the government into different branches to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. This idea was adopted by many modern constitutions.
Impact on Science and Reason
The Enlightenment emphasized the importance of reason and scientific inquiry. Enlightenment thinkers challenged traditional beliefs that were based on superstition or dogma, and instead promoted the use of observation and experimentation to understand the natural world.
The Enlightenment also led to the development of new scientific methods and the rise of modern science. Scientists such as Isaac Newton and Antoine Lavoisier made significant contributions to the fields of physics and chemistry.
Spread and Legacy of the Enlightenment
The ideas of the Enlightenment spread throughout Europe and beyond. They influenced the American Revolution and the French Revolution, and they continue to shape political and social thought today.
The Enlightenment’s legacy includes the development of modern science, the promotion of individual rights and liberties, and the establishment of democratic governments. It is considered one of the most important intellectual movements in Western history.
Q&A: The Enlightenment Icivics Answer Key
What is the Enlightenment?
The Enlightenment was an intellectual movement that emphasized reason, individualism, and scientific inquiry, which flourished in Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries.
Who were some key figures of the Enlightenment?
Prominent Enlightenment figures included Voltaire, John Locke, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and Immanuel Kant, among others.
How did the Enlightenment influence political thought?
The Enlightenment championed ideas of natural rights, limited government, and the separation of powers, which laid the foundation for modern democratic principles.
What was the impact of the Enlightenment on science?
The Enlightenment fostered a belief in the power of reason and scientific observation, leading to advancements in fields such as astronomy, physics, and medicine.
How did the Enlightenment spread beyond Europe?
Enlightenment ideas spread through the works of philosophers, the exchange of letters, and the growth of global trade, influencing intellectual and political movements worldwide.