Atlantic system ap world history – The Atlantic System, a complex web of economic, social, and political interactions that emerged in the 15th century, played a pivotal role in shaping the modern world. Beginning with the European exploration and colonization of the Americas, the Atlantic System connected diverse regions and peoples, leading to profound transformations in economies, societies, and cultures.
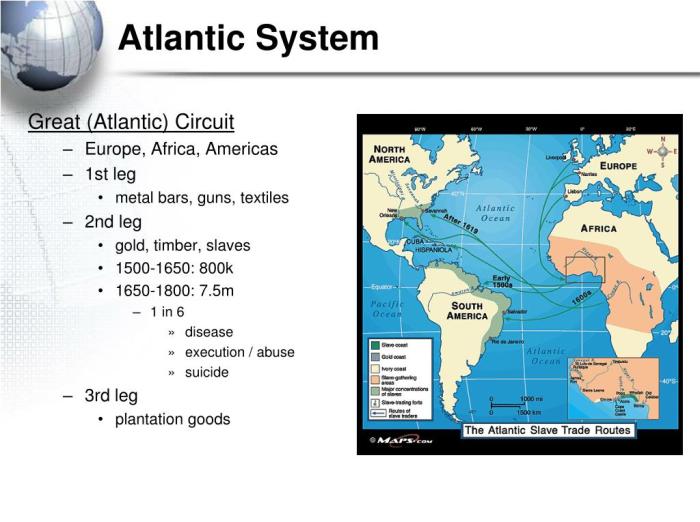
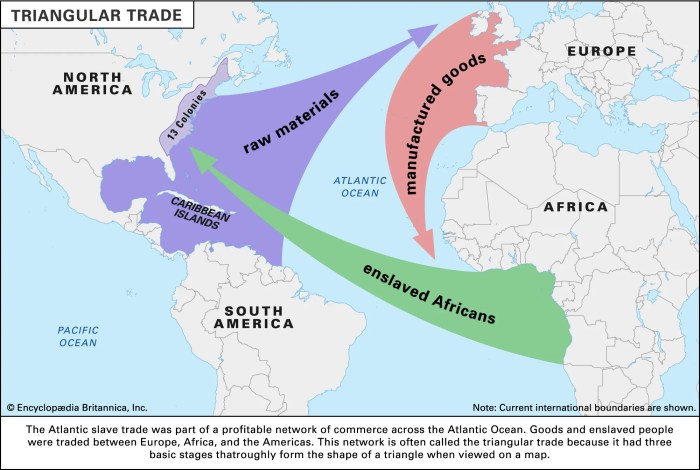
The establishment of trade routes across the Atlantic Ocean facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. European powers, driven by mercantilist policies, sought to extract wealth from their colonies, leading to the development of plantation economies and the transatlantic slave trade.
These economic activities had far-reaching consequences, including the rise of capitalism and the spread of industrialization.
Historical Context
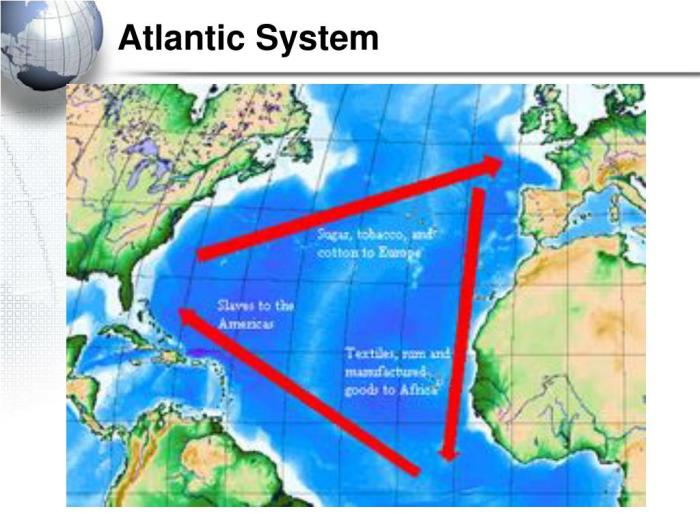
The Atlantic System emerged during the 15th century as European powers embarked on a period of exploration and colonization. Driven by the desire for wealth, resources, and strategic advantage, these powers established colonies in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, creating a complex network of economic, political, and cultural interactions.
Major European Powers and their Motivations
The major European powers involved in the Atlantic System included Portugal, Spain, England, France, and the Netherlands. Each of these powers had its own unique motivations for exploration and colonization, but they all shared a common desire to expand their wealth and power.
- Portugal: Portugal was the first European power to embark on a sustained period of exploration. Motivated by the desire to find a sea route to India, Portuguese explorers established colonies in Africa, Asia, and South America.
- Spain: Spain followed closely behind Portugal in terms of exploration and colonization. Driven by the desire for gold and silver, Spanish explorers established colonies in the Americas, where they exploited the labor of indigenous peoples to extract precious metals.
- England: England entered the Atlantic System later than Portugal and Spain, but quickly became a major player. Motivated by the desire for land and resources, English colonists established settlements in North America, the Caribbean, and India.
- France: France also played a significant role in the Atlantic System. Motivated by the desire to expand its empire and rival England, French colonists established settlements in North America, the Caribbean, and Africa.
- Netherlands: The Netherlands was a latecomer to the Atlantic System, but quickly became a major economic power. Motivated by the desire for trade and profit, Dutch merchants established trading posts and colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
Economic Impact
The Atlantic System, an interconnected global network spanning the Americas, Europe, and Africa, profoundly transformed the economic landscape of the world. This vast network facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and labor, leading to unprecedented economic growth and development.
One of the most significant economic impacts of the Atlantic System was the rise of trade. The exchange of goods between different regions created new markets and stimulated economic activity. European powers established colonies in the Americas and Africa, where they exploited natural resources and established plantations, producing cash crops such as sugar, tobacco, and cotton.
These products were then shipped to Europe, where they were in high demand. In return, European goods, such as manufactured products and luxury items, were exported to the colonies.
Mercantilism
The Atlantic System was also characterized by the rise of mercantilism, an economic theory that emphasized the importance of state intervention in the economy. Mercantilist policies aimed to maximize a nation’s wealth and power by promoting exports and restricting imports.
Governments granted monopolies to favored companies and imposed tariffs on foreign goods to protect domestic industries. Mercantilism played a significant role in shaping the economic development of European nations during this period.
Slave Trade, Atlantic system ap world history
The Atlantic System was inextricably linked to the transatlantic slave trade. The demand for labor on plantations in the Americas led to the forced migration of millions of Africans to the New World. The slave trade was a brutal and inhumane practice that had devastating consequences for African societies.
However, it also contributed to the economic growth of the Americas, as slave labor played a crucial role in the production of cash crops.
Social and Cultural Exchange: Atlantic System Ap World History
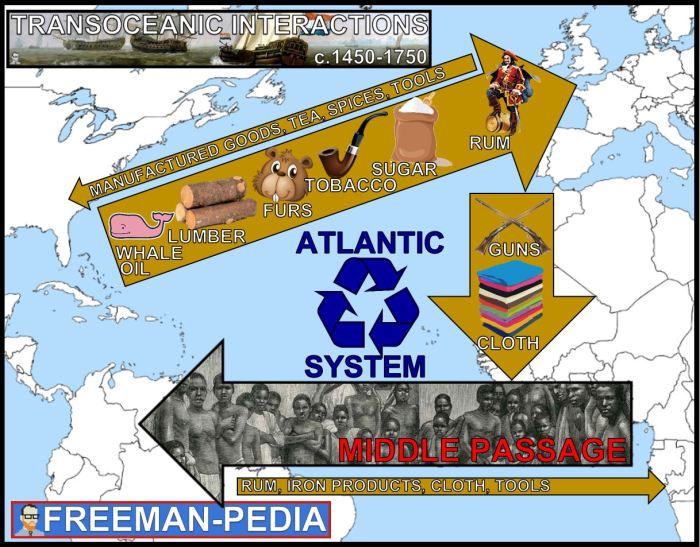
The Atlantic System facilitated extensive social and cultural interactions among different peoples. These exchanges had a profound impact on societies on both sides of the Atlantic.
The forced migration of Africans to the Americas led to the spread of African cultures, traditions, and beliefs throughout the Americas. African slaves brought with them their own languages, music, dance, and art, which influenced the development of new cultural forms in the Americas.
Spread of Ideas
The Atlantic System also facilitated the spread of ideas and technologies. European ideas about government, religion, and science were introduced to the Americas, while American ideas about democracy and independence influenced European thought.
Spread of Technologies
The Atlantic System also led to the spread of new technologies. European technologies, such as firearms and printing presses, were introduced to the Americas, while American technologies, such as the cultivation of corn and potatoes, were introduced to Europe.
Spread of Diseases
The Atlantic System also facilitated the spread of diseases. European diseases, such as smallpox and measles, devastated indigenous populations in the Americas, while American diseases, such as syphilis, were introduced to Europe.
Political and Military Conflicts
The Atlantic System, an interconnected global network spanning centuries, witnessed numerous political and military conflicts that shaped its evolution. These conflicts were driven by a complex interplay of economic, political, and ideological factors, with far-reaching consequences for the participating nations and the wider world.
The struggle for colonial dominance and access to resources was a primary catalyst for conflict within the Atlantic System. European powers, particularly Spain, Portugal, England, France, and the Netherlands, competed fiercely for control of territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
These conflicts often involved the use of force, resulting in the displacement and subjugation of indigenous populations.
Seven Years’ War (1756-1763)
The Seven Years’ War, also known as the French and Indian War in North America, was a global conflict that pitted Great Britain against France, Spain, and their respective allies. The war was primarily fought over colonial territories in North America and India.
The British victory in the war resulted in the acquisition of vast territories in North America and the weakening of French and Spanish power in the region.
American Revolutionary War (1775-1783)
The American Revolutionary War was a conflict between Great Britain and its thirteen colonies in North America. The war was sparked by growing tensions over taxation and representation, and culminated in the Declaration of Independence in 1776. The American victory in the war established the United States of America as an independent nation and weakened British power in the Americas.
Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815)
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of conflicts involving France under Napoleon Bonaparte and various European powers. The wars were primarily driven by Napoleon’s ambitions to expand French power and influence across Europe. The wars had a profound impact on the political landscape of Europe, leading to the redrawing of borders and the rise of new nation-states.
The political and military conflicts within the Atlantic System had far-reaching consequences. They contributed to the rise of nationalism and the decline of colonialism, as well as the emergence of new global powers. The conflicts also had a profound impact on the lives of individuals, leading to displacement, economic disruption, and social upheaval.
Environmental Impact
The Atlantic System had a significant environmental impact, primarily due to the expansion of European powers into the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
One of the most significant impacts was deforestation. European settlers cleared vast areas of forest for agriculture, logging, and urbanization. This deforestation led to soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, and changes in local climates.
Resource Extraction
The Atlantic System also led to the extraction of natural resources, such as minerals, timber, and agricultural products, from the Americas and Africa. This extraction often had negative environmental consequences, including pollution, habitat destruction, and overexploitation of resources.
Introduction of Invasive Species
The Atlantic System also facilitated the introduction of invasive species to new environments. These species, such as rats, rabbits, and plants, often had devastating impacts on local ecosystems, outcompeting native species for resources and causing declines in biodiversity.
Legacy and Impact
The Atlantic System left a profound and lasting impact on the world, shaping the economies, societies, and cultures of continents and civilizations.
Economically, the system created a global network of trade and commerce, leading to the rise of capitalism and the development of new industries and technologies. It also resulted in the exploitation of resources and labor in the Americas and Africa, contributing to the wealth and prosperity of European nations.
Social and Cultural Exchange
The Atlantic System facilitated the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and cultural practices between different parts of the world. This led to the spread of Christianity, the development of new forms of music and art, and the emergence of hybrid cultures that blended European, African, and Native American influences.
Political and Military Conflicts
The Atlantic System also led to political and military conflicts, as European powers competed for control of trade routes and resources. These conflicts included the Seven Years’ War, the American Revolution, and the Napoleonic Wars, which had a significant impact on the political landscape of the world.
Environmental Impact
The Atlantic System had a significant environmental impact, particularly in the Americas. The introduction of European diseases, livestock, and agricultural practices led to the decline of indigenous populations and the destruction of native ecosystems.
Questions Often Asked
What were the major European powers involved in the Atlantic System?
The major European powers involved in the Atlantic System were Spain, Portugal, England, France, and the Netherlands.
What was the role of the slave trade in the Atlantic System?
The slave trade was a central component of the Atlantic System, providing a source of labor for plantations and mines in the Americas. It had a devastating impact on African societies and contributed to the rise of racism and inequality.
How did the Atlantic System contribute to the spread of diseases?
The Atlantic System facilitated the spread of diseases between Europe, Africa, and the Americas. European diseases, such as smallpox and measles, decimated indigenous populations in the Americas, while African diseases, such as yellow fever and malaria, had a significant impact on European settlers.